For teams that are looking for a quick and reliable way to release complex systems, microservices can be an invaluable development practice.
Building and deploying microservices can be done with the Kubernetes container orchestration system, which automates software deployment, scaling, and management. In fact, in many ways, Kubernetes and microservices are a perfect combination, as Kubernetes can handle the orchestration required in order to deploy multiple instances of individual microservices.
So, let’s take a closer look at the steps involved in deploying microservices via Docker containers, and how Kubernetes can be used to manage and scale those microservices.
Introducing Kubernetes for microservices
Kubernetes – also sometimes referred to as “kube”, or k8s – is an open-source container orchestration platform that can be used to automate many of the manual processes required for the deployment, management, and scaling of containerised applications.
Given how difficult it can be to manage individual containers, it shouldn’t be too surprising that so many teams faced with this challenge turn to a trusted tool for deployments in containerised environments, such as Kubernetes.
It is a largely and rapidly growing ecosystem for which crucial services and support are also easily available. This, as far as many teams are concerned, helps to make k8s the best way to deploy microservices.
What are the benefits of Kubernetes for microservices?
So, you now know that “kube” is a reputable choice of platform for the deployment of microservices – but is Kubernetes the optimal fit for your own project?
To aid you in making that decision, here are some of the key advantages Kubernetes can offer for microservices deployment architecture:
- Self-healing: you can’t guarantee that a particular container won’t fail at some point. Fortunately, if that was to come to pass when you use Kubernetes, the platform would simply automatically replace the container, to ensure the application’s continued health
- Declarative configuration management and version control: one can use source control software – such as Git – to control the YAML formatted files storing Kubernetes configurations. The configurations can be applied as a means of creating or updating resources.
- Scalability: you won’t have to worry about compromised performance as a result of an unmanageable load when you incorporate Kubernetes into your microservice deployment strategy. Even at times of high demand, the platform simply horizontally scales the number of containers running a microservice.
- Zero downtime: deploying microservices with Kubernetes also means being able to create additional pods with a newly released image, all without the existing containers being destroyed. Then, with the new containers up and running, teams can just introduce updates and remove old containers, to help guard against any interruptions brought by downtime.
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud: IT teams can easily avoid vendor lock-in with the help of k8s – they can select a cloud platform onto which to place workloads, such as Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Platform.
- Secrets management: if you’re concerned about sensitive details – such as passwords – being exposed in container images, you can help lower this risk using Kubernetes, which supports secret objects with help from the etcd database.
There are various components that can be instrumental in deploying to Kubernetes – including:
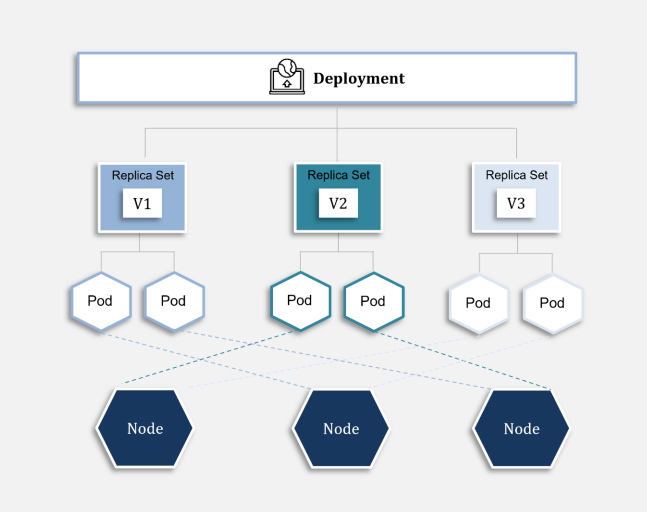
- Pods, which are the smallest deployable units of computing that it is possible to create and manage in Kubernetes. A pod can be described as a group of one or more containers, incorporating shared storage/network resources, and a specification for how the containers are to be run. Pods are used for the storage and management of docker containers.
- ReplicaSets; the purpose of one of these is to keep a stable set of replica pods running at any given time. You may use a ReplicaSet, for instance, to guarantee that a certain number of identical pods will always be available.
- Deployments, which deliver declarative updates for pods and ReplicaSets. In a deployment, it is possible to describe a desired state, with the Deployment Controller changing the actual state to the desired state at a controlled rate. In effect, deployments are an abstraction of ReplicaSets, which in turn, are an abstraction of pods. If, then, you require pods, you shouldn’t create them directly; instead, the creation of deployment objects will lead to the automatic generation of a ReplicaSet and pods.
- Service, which can be described as an abstract way to expose an application running on a set of pods as a network service. The use of Kubernetes won’t require you to modify your application in order to use an unfamiliar service discovery mechanism.
- Secret: with a Kubernetes “Secret”, it is possible to store and manage sensitive information such as passwords, ssh keys, and OAuth keys. The storage of confidential information in a Secret is a safer and more flexible option than placing it verbatim in a pod definition or in a container image.
How can you install and run Kubernetes on a local environment?
There are several means by which you may look to install and run Kubernetes on a local environment. Following the Docker Kubernetes installation, you should go to the Docker settings and enable Kubernetes.
Keeping to the basics, deploying to Kubernetes will essentially entail choosing whether to do so imperatively or declaratively. Imperative Kubernetes deployment involves working on CLI with kubectl commands, while in the case of declarative configuration, you simply need to tell Kubernetes what you want, and the platform will know how to respond.
Later stages of the process of deploying Kubernetes to a local environment include the creation of the Mongo Db Deployment yaml file, the use of k8s Secret Values in the Mongo Deployment yaml file, the running of the Kubernetes manifest file, and the building of Shopper Docker Images.
Allow us to help you get the best out of microservices projects
Would you like to learn more about the finest aspects of microservices deployment strategy and container orchestration, from our own professionals who possess considerable expertise in the deployment of all manner of microservices projects?
If so, please do not hesitate to connect with MindCraft for further discussion today, so that we can provide the right advice, solutions, and support for your specific requirements.